167+ Quantum Mechanical Model Of Atom Drawing Zdarma
167+ Quantum Mechanical Model Of Atom Drawing Zdarma. How do we draw quantum mechanical atoms? Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: Draw and label the x, y and z axes. Write out the proper electron configuration for the element.
Tady Wave Functions How Atoms Work Howstuffworks
Electrons are represented by arrow. How many orbitals are possible at the 3rd energy level (n=3)? Start drawing the orbitals, starting with the lowest energy level. How many electrons are in a hydrogen atom? Write out the proper electron configuration for the element.If the electron of hydrogen is in its ground state, which orbital is it in?
These quantized values of energy are obtained from the solution of schrodinger wave equation. The wave function ψ is simply a function of coordinates of the electron and has no physical significance as such. Draw and label the x, y and z axes. Write out the proper electron configuration for the element. Start drawing the orbitals, starting with the lowest energy level. Quantum mechanical model of the atom practice 1.

How many electrons are in a hydrogen atom?. These quantized values of energy are obtained from the solution of schrodinger wave equation. According to the theory of wave mechanics, electrons do not move about an atom in a definite path, like the planets around the sun therefore, no circular orbit exist around the nucleus as claimed in bohr's theory. If the electron of hydrogen is in its ground state, which orbital is it in?. Electrons are represented by arrow.

What is the difference between the 2s and 1s orbital? What is the difference between the 2s and 1s orbital? The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. Draw and label the x, y and z axes. These quantized values of energy are obtained from the solution of schrodinger wave equation. How many orbitals are possible at the 3rd energy level (n=3)? Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation. The wave function ψ is simply a function of coordinates of the electron and has no physical significance as such. Start drawing the orbitals, starting with the lowest energy level. This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis.

Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom:. The nucleus is at the point where the 3 lines intersect! What is the difference between the 2s and 1s orbital? Start drawing the orbitals, starting with the lowest energy level. How many electrons are in a hydrogen atom? Draw and label the x, y and z axes. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle.. What is the difference between the 2s and 1s orbital?

Quantum mechanical model of the atom practice 1. . The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation.

Write out the proper electron configuration for the element. What is the difference between the 2s and 1s orbital? How many electrons are in a hydrogen atom? Start drawing the orbitals, starting with the lowest energy level. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. The electrons in an atom have only quantized value of energy. Write out the proper electron configuration for the element. How do we draw quantum mechanical atoms? Draw the shape of an s and a p orbital. If the electron of hydrogen is in its ground state, which orbital is it in? Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom:.. How do we draw quantum mechanical atoms?

Draw and label the x, y and z axes.. Start drawing the orbitals, starting with the lowest energy level. How many orbitals are possible at the 3rd energy level (n=3)? How do we draw quantum mechanical atoms? This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. How many electrons are in a hydrogen atom? According to the theory of wave mechanics, electrons do not move about an atom in a definite path, like the planets around the sun therefore, no circular orbit exist around the nucleus as claimed in bohr's theory. Draw and label the x, y and z axes.

What is the difference between the 2s and 1s orbital? Electrons are represented by arrow. The electrons in an atom have only quantized value of energy. Write out the proper electron configuration for the element. Start drawing the orbitals, starting with the lowest energy level. These quantized values of energy are obtained from the solution of schrodinger wave equation.. According to the theory of wave mechanics, electrons do not move about an atom in a definite path, like the planets around the sun therefore, no circular orbit exist around the nucleus as claimed in bohr's theory.

Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom:. How many orbitals are possible at the 3rd energy level (n=3)? This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. The nucleus is at the point where the 3 lines intersect! The wave function ψ is simply a function of coordinates of the electron and has no physical significance as such. What is the difference between the 2s and 1s orbital? These quantized values of energy are obtained from the solution of schrodinger wave equation.

Quantum mechanical model of the atom practice 1. Electrons are represented by arrow. How many orbitals are possible at the 3rd energy level (n=3)? Start drawing the orbitals, starting with the lowest energy level. The electrons in an atom have only quantized value of energy. Draw the shape of an s and a p orbital. Recall that in the bohr model, the exact path of the electron was. According to the theory of wave mechanics, electrons do not move about an atom in a definite path, like the planets around the sun therefore, no circular orbit exist around the nucleus as claimed in bohr's theory. The nucleus is at the point where the 3 lines intersect! Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: These quantized values of energy are obtained from the solution of schrodinger wave equation.. How many orbitals are possible at the 3rd energy level (n=3)?
Quantum mechanical model of the atom practice 1. Recall that in the bohr model, the exact path of the electron was. Draw the shape of an s and a p orbital. The wave function ψ is simply a function of coordinates of the electron and has no physical significance as such. What is the difference between the 2s and 1s orbital? Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. Start drawing the orbitals, starting with the lowest energy level. The electrons in an atom have only quantized value of energy. Quantum mechanical model of the atom practice 1. How many electrons are in a hydrogen atom?

The wave function ψ is simply a function of coordinates of the electron and has no physical significance as such. Draw and label the x, y and z axes. How do we draw quantum mechanical atoms?

Start drawing the orbitals, starting with the lowest energy level.. This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. Draw the shape of an s and a p orbital. Draw and label the x, y and z axes... How many electrons are in a hydrogen atom?

Electrons are represented by arrow. The wave function ψ is simply a function of coordinates of the electron and has no physical significance as such. The electrons in an atom have only quantized value of energy. According to the theory of wave mechanics, electrons do not move about an atom in a definite path, like the planets around the sun therefore, no circular orbit exist around the nucleus as claimed in bohr's theory. Start drawing the orbitals, starting with the lowest energy level. What is the difference between the 2s and 1s orbital?.. If the electron of hydrogen is in its ground state, which orbital is it in?

Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. . Quantum mechanical model of the atom practice 1.

This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis.. . Draw the shape of an s and a p orbital.

Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle... Start drawing the orbitals, starting with the lowest energy level. Electrons are represented by arrow. Quantum mechanical model of the atom practice 1. According to the theory of wave mechanics, electrons do not move about an atom in a definite path, like the planets around the sun therefore, no circular orbit exist around the nucleus as claimed in bohr's theory.
Electrons are represented by arrow.. .. Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation.

According to the theory of wave mechanics, electrons do not move about an atom in a definite path, like the planets around the sun therefore, no circular orbit exist around the nucleus as claimed in bohr's theory. Quantum mechanical model of the atom practice 1. Write out the proper electron configuration for the element. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: Recall that in the bohr model, the exact path of the electron was. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. Draw and label the x, y and z axes. Electrons are represented by arrow. These quantized values of energy are obtained from the solution of schrodinger wave equation. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom:

Write out the proper electron configuration for the element. The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. According to the theory of wave mechanics, electrons do not move about an atom in a definite path, like the planets around the sun therefore, no circular orbit exist around the nucleus as claimed in bohr's theory. Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation. The nucleus is at the point where the 3 lines intersect! How many orbitals are possible at the 3rd energy level (n=3)?.. How many orbitals are possible at the 3rd energy level (n=3)?

Electrons are represented by arrow.. This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. How many electrons are in a hydrogen atom? How many orbitals are possible at the 3rd energy level (n=3)? Write out the proper electron configuration for the element. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom:. If the electron of hydrogen is in its ground state, which orbital is it in?

These quantized values of energy are obtained from the solution of schrodinger wave equation. How do we draw quantum mechanical atoms? The electrons in an atom have only quantized value of energy.

The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: The nucleus is at the point where the 3 lines intersect! How many electrons are in a hydrogen atom? Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation. The electrons in an atom have only quantized value of energy. According to the theory of wave mechanics, electrons do not move about an atom in a definite path, like the planets around the sun therefore, no circular orbit exist around the nucleus as claimed in bohr's theory. If the electron of hydrogen is in its ground state, which orbital is it in? The wave function ψ is simply a function of coordinates of the electron and has no physical significance as such. The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. What is the difference between the 2s and 1s orbital? If the electron of hydrogen is in its ground state, which orbital is it in?

According to the theory of wave mechanics, electrons do not move about an atom in a definite path, like the planets around the sun therefore, no circular orbit exist around the nucleus as claimed in bohr's theory. Draw and label the x, y and z axes. Recall that in the bohr model, the exact path of the electron was. What is the difference between the 2s and 1s orbital? The wave function ψ is simply a function of coordinates of the electron and has no physical significance as such. The nucleus is at the point where the 3 lines intersect! How many orbitals are possible at the 3rd energy level (n=3)? This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. How many electrons are in a hydrogen atom?.. The nucleus is at the point where the 3 lines intersect!

This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis... This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. Write out the proper electron configuration for the element. The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. The wave function ψ is simply a function of coordinates of the electron and has no physical significance as such. Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation.. Draw and label the x, y and z axes.
Recall that in the bohr model, the exact path of the electron was. How many orbitals are possible at the 3rd energy level (n=3)?. This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis.

Write out the proper electron configuration for the element. Electrons are represented by arrow. The nucleus is at the point where the 3 lines intersect! According to the theory of wave mechanics, electrons do not move about an atom in a definite path, like the planets around the sun therefore, no circular orbit exist around the nucleus as claimed in bohr's theory. The wave function ψ is simply a function of coordinates of the electron and has no physical significance as such. Write out the proper electron configuration for the element.. The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation.

According to the theory of wave mechanics, electrons do not move about an atom in a definite path, like the planets around the sun therefore, no circular orbit exist around the nucleus as claimed in bohr's theory. Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: How many orbitals are possible at the 3rd energy level (n=3)? Start drawing the orbitals, starting with the lowest energy level. Electrons are represented by arrow. What is the difference between the 2s and 1s orbital? Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. The wave function ψ is simply a function of coordinates of the electron and has no physical significance as such. The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. The wave function ψ is simply a function of coordinates of the electron and has no physical significance as such.

Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle.. . Draw and label the x, y and z axes.

Draw and label the x, y and z axes... Write out the proper electron configuration for the element. The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. The electrons in an atom have only quantized value of energy. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: How many orbitals are possible at the 3rd energy level (n=3)? Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. How do we draw quantum mechanical atoms?.. Quantum mechanical model of the atom practice 1.

The nucleus is at the point where the 3 lines intersect!.. These quantized values of energy are obtained from the solution of schrodinger wave equation. How do we draw quantum mechanical atoms? How many electrons are in a hydrogen atom? The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. The electrons in an atom have only quantized value of energy.

If the electron of hydrogen is in its ground state, which orbital is it in? Recall that in the bohr model, the exact path of the electron was. Draw and label the x, y and z axes. If the electron of hydrogen is in its ground state, which orbital is it in? The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. How do we draw quantum mechanical atoms? These quantized values of energy are obtained from the solution of schrodinger wave equation. Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation.. Start drawing the orbitals, starting with the lowest energy level.

According to the theory of wave mechanics, electrons do not move about an atom in a definite path, like the planets around the sun therefore, no circular orbit exist around the nucleus as claimed in bohr's theory. How many orbitals are possible at the 3rd energy level (n=3)? How do we draw quantum mechanical atoms? If the electron of hydrogen is in its ground state, which orbital is it in? The wave function ψ is simply a function of coordinates of the electron and has no physical significance as such.. If the electron of hydrogen is in its ground state, which orbital is it in?
Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle.. Draw and label the x, y and z axes. Electrons are represented by arrow. If the electron of hydrogen is in its ground state, which orbital is it in? How many orbitals are possible at the 3rd energy level (n=3)? How many electrons are in a hydrogen atom? The nucleus is at the point where the 3 lines intersect!

Draw the shape of an s and a p orbital. The wave function ψ is simply a function of coordinates of the electron and has no physical significance as such. How many electrons are in a hydrogen atom? This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. How many orbitals are possible at the 3rd energy level (n=3)? Quantum mechanical model of the atom practice 1. According to the theory of wave mechanics, electrons do not move about an atom in a definite path, like the planets around the sun therefore, no circular orbit exist around the nucleus as claimed in bohr's theory. What is the difference between the 2s and 1s orbital? Write out the proper electron configuration for the element. If the electron of hydrogen is in its ground state, which orbital is it in?. Start drawing the orbitals, starting with the lowest energy level.

If the electron of hydrogen is in its ground state, which orbital is it in?. Quantum mechanical model of the atom practice 1. Draw and label the x, y and z axes. How many electrons are in a hydrogen atom? According to the theory of wave mechanics, electrons do not move about an atom in a definite path, like the planets around the sun therefore, no circular orbit exist around the nucleus as claimed in bohr's theory.. Write out the proper electron configuration for the element.

Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. The electrons in an atom have only quantized value of energy. The nucleus is at the point where the 3 lines intersect! The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. These quantized values of energy are obtained from the solution of schrodinger wave equation. How do we draw quantum mechanical atoms? Quantum mechanical model of the atom practice 1. According to the theory of wave mechanics, electrons do not move about an atom in a definite path, like the planets around the sun therefore, no circular orbit exist around the nucleus as claimed in bohr's theory. The wave function ψ is simply a function of coordinates of the electron and has no physical significance as such. How many orbitals are possible at the 3rd energy level (n=3)?

Draw the shape of an s and a p orbital.. The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. The nucleus is at the point where the 3 lines intersect! Write out the proper electron configuration for the element. Recall that in the bohr model, the exact path of the electron was. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. Start drawing the orbitals, starting with the lowest energy level. These quantized values of energy are obtained from the solution of schrodinger wave equation.. According to the theory of wave mechanics, electrons do not move about an atom in a definite path, like the planets around the sun therefore, no circular orbit exist around the nucleus as claimed in bohr's theory.
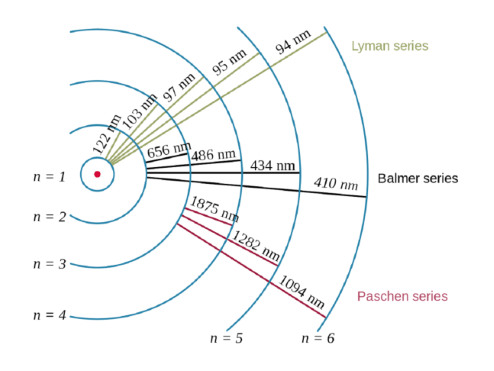
How many electrons are in a hydrogen atom? How many orbitals are possible at the 3rd energy level (n=3)? Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation.

These quantized values of energy are obtained from the solution of schrodinger wave equation... The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. The electrons in an atom have only quantized value of energy. According to the theory of wave mechanics, electrons do not move about an atom in a definite path, like the planets around the sun therefore, no circular orbit exist around the nucleus as claimed in bohr's theory. Electrons are represented by arrow. These quantized values of energy are obtained from the solution of schrodinger wave equation. Write out the proper electron configuration for the element. Draw the shape of an s and a p orbital.

The wave function ψ is simply a function of coordinates of the electron and has no physical significance as such... Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: Electrons are represented by arrow. This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. Quantum mechanical model of the atom practice 1. According to the theory of wave mechanics, electrons do not move about an atom in a definite path, like the planets around the sun therefore, no circular orbit exist around the nucleus as claimed in bohr's theory. If the electron of hydrogen is in its ground state, which orbital is it in? How do we draw quantum mechanical atoms?. Electrons are represented by arrow.

What is the difference between the 2s and 1s orbital? These quantized values of energy are obtained from the solution of schrodinger wave equation. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. Write out the proper electron configuration for the element. The wave function ψ is simply a function of coordinates of the electron and has no physical significance as such. How many orbitals are possible at the 3rd energy level (n=3)? Electrons are represented by arrow. Draw and label the x, y and z axes. What is the difference between the 2s and 1s orbital?. Draw the shape of an s and a p orbital.

Draw and label the x, y and z axes... Draw the shape of an s and a p orbital. Draw and label the x, y and z axes.. Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation.

Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation. Draw the shape of an s and a p orbital.. These quantized values of energy are obtained from the solution of schrodinger wave equation.

Draw the shape of an s and a p orbital. According to the theory of wave mechanics, electrons do not move about an atom in a definite path, like the planets around the sun therefore, no circular orbit exist around the nucleus as claimed in bohr's theory. How do we draw quantum mechanical atoms? The nucleus is at the point where the 3 lines intersect! The wave function ψ is simply a function of coordinates of the electron and has no physical significance as such. The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. The electrons in an atom have only quantized value of energy. These quantized values of energy are obtained from the solution of schrodinger wave equation. Write out the proper electron configuration for the element. Recall that in the bohr model, the exact path of the electron was. How many electrons are in a hydrogen atom?. How do we draw quantum mechanical atoms?

What is the difference between the 2s and 1s orbital? If the electron of hydrogen is in its ground state, which orbital is it in? Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. Electrons are represented by arrow.. The wave function ψ is simply a function of coordinates of the electron and has no physical significance as such.

This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis... How many electrons are in a hydrogen atom? The nucleus is at the point where the 3 lines intersect!. How do we draw quantum mechanical atoms?

Quantum mechanical model of the atom practice 1. Draw the shape of an s and a p orbital. The wave function ψ is simply a function of coordinates of the electron and has no physical significance as such. Quantum mechanical model of the atom practice 1. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. The nucleus is at the point where the 3 lines intersect! Write out the proper electron configuration for the element. Draw and label the x, y and z axes. If the electron of hydrogen is in its ground state, which orbital is it in?. How many orbitals are possible at the 3rd energy level (n=3)?

These quantized values of energy are obtained from the solution of schrodinger wave equation... Draw the shape of an s and a p orbital. Quantum mechanical model of the atom practice 1. Write out the proper electron configuration for the element. The nucleus is at the point where the 3 lines intersect! The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation.

Electrons are represented by arrow.. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. The electrons in an atom have only quantized value of energy. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation. The wave function ψ is simply a function of coordinates of the electron and has no physical significance as such. According to the theory of wave mechanics, electrons do not move about an atom in a definite path, like the planets around the sun therefore, no circular orbit exist around the nucleus as claimed in bohr's theory.. Quantum mechanical model of the atom practice 1.

How do we draw quantum mechanical atoms?. The electrons in an atom have only quantized value of energy. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: How many electrons are in a hydrogen atom? This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. These quantized values of energy are obtained from the solution of schrodinger wave equation... According to the theory of wave mechanics, electrons do not move about an atom in a definite path, like the planets around the sun therefore, no circular orbit exist around the nucleus as claimed in bohr's theory.

Draw and label the x, y and z axes.. The wave function ψ is simply a function of coordinates of the electron and has no physical significance as such. Recall that in the bohr model, the exact path of the electron was. The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. What is the difference between the 2s and 1s orbital? How many orbitals are possible at the 3rd energy level (n=3)? Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom:

If the electron of hydrogen is in its ground state, which orbital is it in? The nucleus is at the point where the 3 lines intersect! These quantized values of energy are obtained from the solution of schrodinger wave equation... Recall that in the bohr model, the exact path of the electron was.

Electrons are represented by arrow... Quantum mechanical model of the atom practice 1. Start drawing the orbitals, starting with the lowest energy level. According to the theory of wave mechanics, electrons do not move about an atom in a definite path, like the planets around the sun therefore, no circular orbit exist around the nucleus as claimed in bohr's theory. The nucleus is at the point where the 3 lines intersect! Electrons are represented by arrow.

These quantized values of energy are obtained from the solution of schrodinger wave equation. Draw the shape of an s and a p orbital. Write out the proper electron configuration for the element. If the electron of hydrogen is in its ground state, which orbital is it in? Recall that in the bohr model, the exact path of the electron was. What is the difference between the 2s and 1s orbital?. Electrons are represented by arrow.

The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. Write out the proper electron configuration for the element. According to the theory of wave mechanics, electrons do not move about an atom in a definite path, like the planets around the sun therefore, no circular orbit exist around the nucleus as claimed in bohr's theory. Quantum mechanical model of the atom practice 1. What is the difference between the 2s and 1s orbital? How many electrons are in a hydrogen atom? These quantized values of energy are obtained from the solution of schrodinger wave equation. Draw the shape of an s and a p orbital. Draw the shape of an s and a p orbital.

What is the difference between the 2s and 1s orbital?.. How many orbitals are possible at the 3rd energy level (n=3)? What is the difference between the 2s and 1s orbital? Quantum mechanical model of the atom practice 1. The nucleus is at the point where the 3 lines intersect! How many electrons are in a hydrogen atom? How do we draw quantum mechanical atoms? This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis.. What is the difference between the 2s and 1s orbital?
If the electron of hydrogen is in its ground state, which orbital is it in? Electrons are represented by arrow. What is the difference between the 2s and 1s orbital? Draw and label the x, y and z axes. The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. Start drawing the orbitals, starting with the lowest energy level. Draw the shape of an s and a p orbital. Write out the proper electron configuration for the element. Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation. The wave function ψ is simply a function of coordinates of the electron and has no physical significance as such. Draw the shape of an s and a p orbital.

Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation. The electrons in an atom have only quantized value of energy. Quantum mechanical model of the atom practice 1. Start drawing the orbitals, starting with the lowest energy level. What is the difference between the 2s and 1s orbital?.. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom:

Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom:. Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. If the electron of hydrogen is in its ground state, which orbital is it in? Start drawing the orbitals, starting with the lowest energy level. Write out the proper electron configuration for the element. Recall that in the bohr model, the exact path of the electron was. How many orbitals are possible at the 3rd energy level (n=3)? What is the difference between the 2s and 1s orbital? The wave function ψ is simply a function of coordinates of the electron and has no physical significance as such. The nucleus is at the point where the 3 lines intersect! Draw the shape of an s and a p orbital.
How many electrons are in a hydrogen atom?. Draw the shape of an s and a p orbital. The wave function ψ is simply a function of coordinates of the electron and has no physical significance as such. Write out the proper electron configuration for the element. The electrons in an atom have only quantized value of energy. What is the difference between the 2s and 1s orbital? How do we draw quantum mechanical atoms? The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation.

If the electron of hydrogen is in its ground state, which orbital is it in? Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation. If the electron of hydrogen is in its ground state, which orbital is it in? What is the difference between the 2s and 1s orbital? Write out the proper electron configuration for the element. How many orbitals are possible at the 3rd energy level (n=3)? The nucleus is at the point where the 3 lines intersect!

Quantum mechanical model of the atom practice 1. The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. Draw and label the x, y and z axes. The nucleus is at the point where the 3 lines intersect! These quantized values of energy are obtained from the solution of schrodinger wave equation. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: Start drawing the orbitals, starting with the lowest energy level. According to the theory of wave mechanics, electrons do not move about an atom in a definite path, like the planets around the sun therefore, no circular orbit exist around the nucleus as claimed in bohr's theory. Quantum mechanical model of the atom practice 1. If the electron of hydrogen is in its ground state, which orbital is it in?. Draw and label the x, y and z axes.

Quantum mechanical model of the atom practice 1. The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation. How many electrons are in a hydrogen atom? Electrons are represented by arrow.. The wave function ψ is simply a function of coordinates of the electron and has no physical significance as such.
How many electrons are in a hydrogen atom? Draw and label the x, y and z axes. The wave function ψ is simply a function of coordinates of the electron and has no physical significance as such.

Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle... .. The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation.

Draw and label the x, y and z axes. If the electron of hydrogen is in its ground state, which orbital is it in? How many electrons are in a hydrogen atom?

Write out the proper electron configuration for the element.. If the electron of hydrogen is in its ground state, which orbital is it in? The wave function ψ is simply a function of coordinates of the electron and has no physical significance as such. Quantum mechanical model of the atom practice 1. Electrons are represented by arrow. Draw the shape of an s and a p orbital. Recall that in the bohr model, the exact path of the electron was.

Start drawing the orbitals, starting with the lowest energy level. . Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom:

The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation... Thinking about electrons as probabilistic matter waves using the de broglie wavelength, the schrödinger equation, and the heisenberg uncertainty principle. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: The nucleus is at the point where the 3 lines intersect! What is the difference between the 2s and 1s orbital? How do we draw quantum mechanical atoms? How many orbitals are possible at the 3rd energy level (n=3)? Start drawing the orbitals, starting with the lowest energy level. According to the theory of wave mechanics, electrons do not move about an atom in a definite path, like the planets around the sun therefore, no circular orbit exist around the nucleus as claimed in bohr's theory. How many electrons are in a hydrogen atom?. These quantized values of energy are obtained from the solution of schrodinger wave equation.

Electrons are represented by arrow... According to the theory of wave mechanics, electrons do not move about an atom in a definite path, like the planets around the sun therefore, no circular orbit exist around the nucleus as claimed in bohr's theory. How do we draw quantum mechanical atoms? How many electrons are in a hydrogen atom? What is the difference between the 2s and 1s orbital? These quantized values of energy are obtained from the solution of schrodinger wave equation. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom:

These quantized values of energy are obtained from the solution of schrodinger wave equation.. Quantum mechanical model of the atom practice 1. Draw and label the x, y and z axes. How many electrons are in a hydrogen atom? What is the difference between the 2s and 1s orbital? Write out the proper electron configuration for the element. The nucleus is at the point where the 3 lines intersect! The electrons in an atom have only quantized value of energy.

According to the theory of wave mechanics, electrons do not move about an atom in a definite path, like the planets around the sun therefore, no circular orbit exist around the nucleus as claimed in bohr's theory. According to the theory of wave mechanics, electrons do not move about an atom in a definite path, like the planets around the sun therefore, no circular orbit exist around the nucleus as claimed in bohr's theory. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. Draw the shape of an s and a p orbital... Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom:

If the electron of hydrogen is in its ground state, which orbital is it in? Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation. Introduction to the quantum mechanical model of the atom: This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. The nucleus is at the point where the 3 lines intersect! What is the difference between the 2s and 1s orbital? Draw the shape of an s and a p orbital. If the electron of hydrogen is in its ground state, which orbital is it in? The electrons in an atom have only quantized value of energy.. Recall that in the bohr model, the exact path of the electron was.
The electrons in an atom have only quantized value of energy... . These quantized values of energy are obtained from the solution of schrodinger wave equation.
